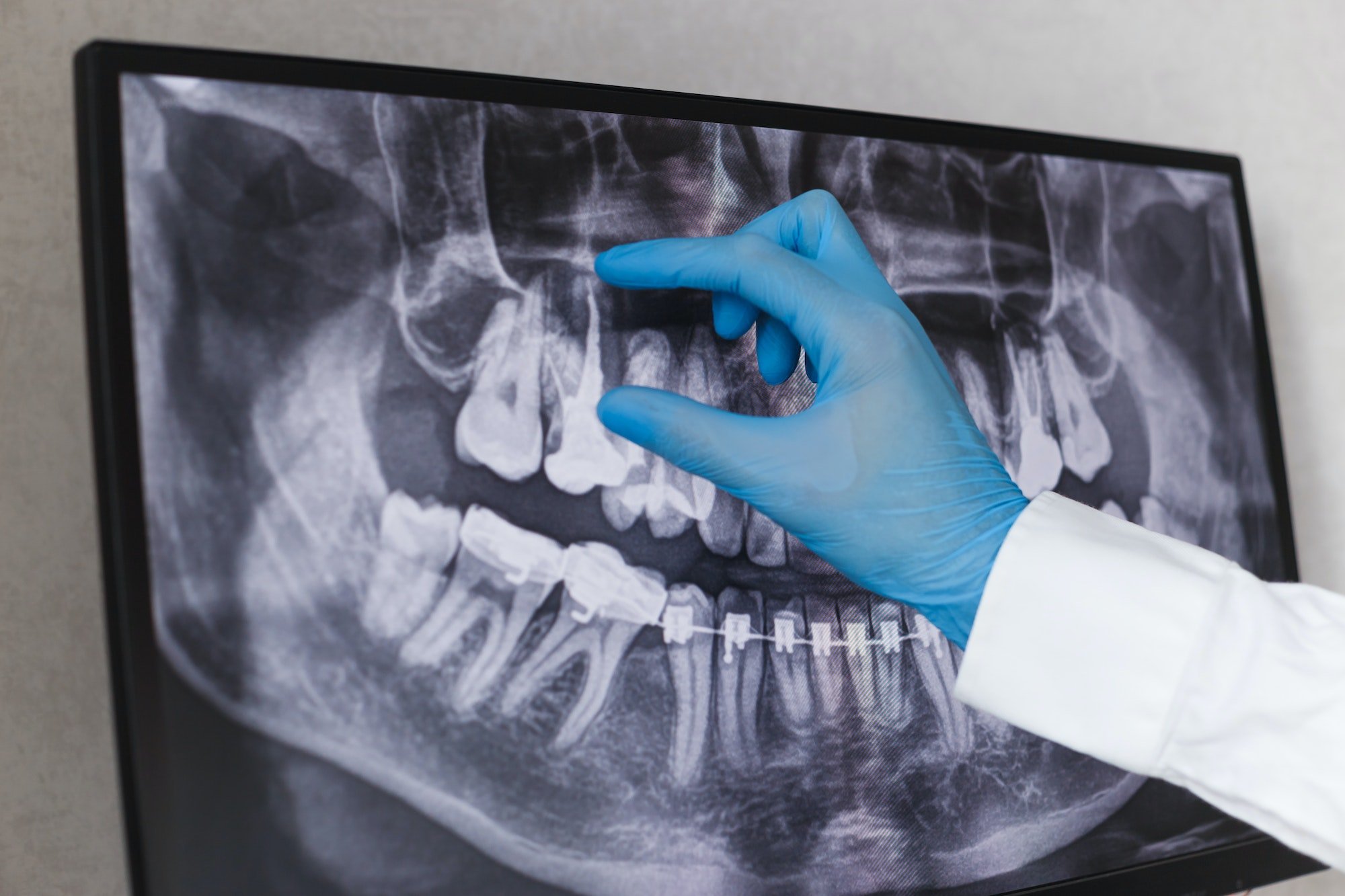
Calcified root canals are a highly prevalent problem among older generations. These buildups of calcium within the root channels can impact the pulp, blood vessels, and nerves throughout the tooth, ultimately leading to a greater risk of tooth pain, tooth infections, and decay. When present, they also inhibit the dentist’s ability to perform regular root canal treatments, meaning that an endodontist must correct the issue. Aging populations are more at risk of dental trauma, as calcium buildup is usually an inhibitory response to the present trauma. With calcified root canals, this issue can make any signs of trauma worse for the individual.
Luckily, endodontists are often prepared for these scenarios, as they have many instruments at hand to remove the calcification and leave behind a healthier tooth. Patients need to reach out to an endodontist if they have calcified root canals because by removing the presence of overactive calcium, the tooth’s pulp and root channels can be preserved.
What Are Calcified Root Canals?
Calcified root canals, also known as pulp sclerosis, occur when there are increasing amounts of calcium within the root canals. When this happens, the canal space is significantly decreased and places pressure along the pulp and blood vessels within the tooth. It’s a natural process produced by the body and is considered both pathological and physiological. When patients experience calcified root canals, severe pain, swelling, and infection, it develops gradually over time, and when it progresses in advanced stages, treatment for this condition can be challenging.
However, when it comes to treating calcified canals, it highly depends on the stage of the calcification, the root canals affected, and the stage of tooth decay or trauma affecting the tooth. Patients attempting to diagnose calcified root canals may find it difficult to do so, as often calcified canals produce many similar symptoms as with cavities, toothaches, and pulpitis. The outer appearance of the tooth looks dark and yellow and can often coincide with other dental issues. However, there are some patients that can have calcified root canals but don’t experience symptoms. In these cases, the calcified root canal can develop gradually over time and cause advanced stages of decay, which is why we emphasize regular annual dental visits.
Should You Have Root Canal Treatment on a Wisdom Tooth?
What Causes The Tooth To Calcify?
The most common cause for calcified canals is trauma to the tooth’s apex and pulp. In most cases, dental trauma often creates a reactionary deposit of calcium to allow the tooth’s structure to regenerate naturally and attempt to heal the inner pulp chambers. However, most often, this deposit of calcium is harmful to the tooth, restricting the natural pulp chambers and root canals and restricting the pulp’s ability to heal. In these cases, trauma is most often experienced by those 65 and old due to issues maintaining proper calcium and vitamin D levels, but it can also be experienced from accidents and sports injuries. However, calcification occurs quite often, as up to 24% of teeth impacted by trauma end up partially or completely calcifying, leading to years of undetected decay.
For endodontists treating these root canals, the biggest challenge present is cleaning out the canal space, as one of the largest factors determining the success of a procedure is the amount of canal space a dentist is able to work with to remove signs of infection. When treating calcified root canals, it requires an intense amount of technical skill to clean out the calcium without impacting the pulp and nerves. Because of its complexity, the American Association of Endodontics sets out clear treatment protocols and examination methods for finding, cleaning, and preserving healthy tissue pulp within the affected tooth. The focus of treating calcified root canals is to make sure that the tooth’s intact, the pulp is healthy, and that the root canals are clear of infection to help avoid the need for extractions.
Methods For Finding and Treating Calcified Teeth
On the surface of the procedure, it can be difficult to find calcification if it’s deep within the root canals. However, our available technology allows us to visualize and diagnose calcified teeth easily, as, through various methods, the root canals can be observed and help locate any possible signs of infection, decay, or other blockages within the systems. With the use of various forms of technology, many endodontists are able to get to these accessways through the use of:
- CBCT Technology: CBCT technology, also known as cone-beam computed technology, uses cone-shaped X-ray beans to capture visual data from the tooth’s internal structure. This method allows endodontists to observe the underlying jawbone, tooth root canals, and soft pulp tissues. If calcified canals are present, then they may appear in the scans.
- Digital Impressions: Digital impressions also allow endodontists to help transfer medical data about the tooth and thus give endodontists a closer look at the tooth’s internal structures. These files can be manipulated and superimposed onto the CBCT scans to align root canal arches and create a guide for treatment.
- 3D Printing: In cases where the calcified canals are complex, 3D printing can be used as a template guide for creating proposed pathways for removing the calcified areas from the inner chambers. However, these methods are mostly used for restorative methods for cases where the root canals cannot be saved.
- Microscopes: Microscopes are used during the treatment process and often help endodontists perform their treatments accurately to increase the success of the procedure while working inside the tooth.
With these pieces of technology, endodontists are often able to better locate the calcified canal, have direct contact with the calcification, and then use techniques to remove the calcification and any remaining bacteria left behind. Once the calcification is removed, then a normal root canal procedure can be used to remove infection, bacteria and help repair any signs of inner trauma within the tooth. Once completely sealed with rubber or plastic, the tooth can be repaired, analyzed further for healing, and function normally.
For more information about getting a calcification removal treatment, contacting your local endodontist is the first place to go for treatment.
Why Root Canal Treatment for Broken Teeth Might be Necessary?