Intro
Welcome to the encyclopedia of toothaches! Toothaches are a common dental issue that can cause pain and discomfort in or around the teeth. They can be caused by a variety of factors, including tooth decay, gum disease, sinusitis, abscesses, tonsillitis, dental treatment-related issues, and more. The symptoms of a toothache may vary depending on the cause but can include pain when biting or chewing, sensitivity to hot or cold foods or drinks, swelling around the tooth, and constant or intermittent throbbing pain. Home remedies, such as rinsing with warm salt water and taking over-the-counter pain medication, can provide temporary relief, but it may become necessary to see a dentist for a proper diagnosis and treatment. Dental procedures, such as filling a cavity or root canal therapy, may be necessary to alleviate the pain and stop complications. To prevent toothaches, it is important to practice good oral hygiene and avoid sugary foods and drinks. In this encyclopedia, we will explore the different types of toothaches, their causes, symptoms, home remedies, treatments, and prevention measures. By understanding the different types of toothaches and how to address them properly, you can take control of your oral health and reduce the risk of toothaches in the future.
Table of Contents
Dental Treatment

Dental treatments are designed to improve the health and appearance of your teeth, but sometimes they can cause toothaches as a side effect. These toothaches may be temporary and resolve on their own, or they may require additional treatment. In this category, you will find information about the different types of dental treatments that can cause toothaches and how to manage them. It is important to remember that toothaches caused by dental treatments are usually a sign that something is wrong and should not be ignored. If you are experiencing a toothache after dental treatment, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Crown

What are the causes of this toothache?
A crown is a dental restoration that covers the entire surface of the tooth. Toothaches related to crowns may be caused by sensitivity to the materials used in the crown, irritation of the nerve inside the tooth, infection of the tooth or surrounding tissues, or pressure on the tooth caused by the crown.
What are the symptoms of this toothache?
The main symptom of a crown-related toothache is swelling and redness around the gums. You may also experience pain when biting or chewing, sensitivity to hot or cold foods or drinks, or discomfort when the crown is touched.
What will irritate this toothache?
Anything that irritates the tooth or surrounding tissues, such as eating or drinking hot or cold foods or beverages, may exacerbate the pain of a crown-related toothache.
How long will this toothache last?
The length of a crown-related toothache will depend on the underlying cause and how quickly it is treated. If left untreated, the toothache may persist or even worsen.
What are the home remedies for this toothache?
There are no effective home remedies for crown-related toothaches. It is important to see a dentist as soon as possible to receive appropriate treatment.
When should you go see a dentist for this toothache?
If you are experiencing a toothache and suspect you may have a problem with a crown, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible. A crown-related toothache can be a sign of a more serious problem that requires immediate attention.
How is this toothache diagnosed?
A dentist can diagnose a crown-related toothache by examining the crown and performing a physical examination. They may also take X-rays to assess the condition of the tooth and surrounding tissue.
What are the possible dental treatments for this toothache?
The treatment for a crown-related toothache will depend on the underlying cause. Options may include adjusting the crown, replacing the crown, or performing a root canal.
What are some complications that result from a lack of treatment for this toothache?
If a crown-related toothache is not treated, it can lead to further complications, such as decay or damage to the tooth or the spread of infection.
How do you prevent this toothache?
To prevent crown-related toothaches, it is important to follow the instructions of your dentist when getting a crown.
Dry Socket

What are the causes of this toothache?
Dry Socket is a condition that occurs after a tooth extraction, such as the removal of a wisdom tooth. It is caused by the loss of the blood clot that forms in the socket after an extraction, which exposes the bone and nerves in the socket to the air and food. This can cause severe pain and other symptoms.
What are the symptoms of this toothache?
The main symptom of a dry socket-related toothache is severe pain. You may also experience a bad taste and unpleasant odor in the mouth.
What will irritate this toothache?
Anything that irritates the exposed bone and nerves in the socket, such as eating or drinking hot or cold foods or beverages, may exacerbate the pain of a dry socket-related toothache.
How long will this toothache last?
The length of a dry socket-related toothache will depend on the severity of the condition and how quickly it is treated. If left untreated, the toothache may persist or even worsen.
What are the home remedies for this toothache?
There are no effective home remedies for a dry socket-related toothache. It is important to see a dentist as soon as possible to receive appropriate treatment.
When should you go see a dentist for this toothache?
If you are experiencing a toothache after tooth extraction and suspect you may have a dry socket, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible. Dry sockets can be very painful and can cause other complications if not treated promptly.
How is this toothache diagnosed?
A dentist can diagnose a dry socket by examining the socket and performing a physical examination.
What are the possible dental treatments for this toothache?
The treatment for a dry socket will depend on the severity of the condition. Options may include cleaning the socket, prescribing pain medication, and packing the socket with a medicated dressing.
What are some complications that result from a lack of treatment for this toothache?
If a dry socket is not treated, it can lead to further complications, such as infection or a delay in healing.
How do you prevent this toothache?
To prevent dry sockets and the resulting toothaches, it is important to follow the instructions of your dentist or oral surgeon after tooth extraction. This may include avoiding strenuous activity, not smoking, and avoiding certain foods and drinks. Your dentist may also prescribe antibiotics to help prevent infection.
Loose Fillings
What are the causes of this toothache?
Loose fillings are caused by wear and tear on the filling material or by the decay around the filling. Fillings can also become loose if they are not properly placed or if the tooth has changed shape since the filling was placed.
What are the symptoms of this toothache?
The main symptom of a loose filling-related toothache is constant or intermittent pain. You may also experience sensitivity to hot or cold foods or drinks or sensitivity when biting or chewing.
What will irritate this toothache?
Anything that puts pressure on the loose filling, such as eating or drinking hot or cold foods or beverages, may exacerbate the pain of a loose filling-related toothache.
How long will this toothache last?
The length of a loose filling-related toothache will depend on the severity of the problem and how quickly it is treated. If left untreated, the toothache may persist or even worsen.
What are the home remedies for this toothache?
There are no effective home remedies for a loose filling-related toothache. It is important to see a dentist as soon as possible to receive appropriate treatment.
When should you go see a dentist for this toothache?
If you are experiencing a toothache and suspect you may have a loose filling, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible. A loose filling can cause further damage to the tooth if not treated promptly.
How is this toothache diagnosed?
A dentist can diagnose a loose filling by examining the filling and performing a physical examination. They may also take X-rays to assess the condition of the tooth and surrounding tissue.
What are the possible dental treatments for this toothache?
The treatment for a loose filling will depend on the severity of the problem. Options may include replacing the filling, performing a root canal, or extracting the tooth.
What are some complications that result from a lack of treatment for this toothache?
If a loose filling is not treated, it can lead to further complications, such as decay or damage to the tooth or the spread of infection.
How do you prevent this toothache?
To prevent loose fillings and the resulting toothaches, it is important to practice good oral hygiene, such as brushing your teeth twice a day and flossing daily. You should also visit your dentist regularly for cleanings and checkups. If you have a filling that is causing discomfort or sensitivity, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible to have it checked and potentially replaced.
Root Canal
What are the causes of this toothache?
A root canal is a dental procedure that involves removing the infected or damaged tissue inside a tooth (the pulp) and cleaning out the inside of the tooth. Toothaches related to root canals may be caused by an infection or inflammation of the pulp or by damage to the tooth.
What are the symptoms of this toothache?
The main symptom of a root canal-related toothache is pain. You may also experience sensitivity to hot or cold foods or drinks or discomfort when biting or chewing.
What will irritate this toothache?
Anything that puts pressure on the tooth, such as eating or drinking hot or cold foods or beverages, may exacerbate the pain of a root canal-related toothache.
How long will this toothache last?
The length of a root canal-related toothache will depend on the severity of the infection or damage to the tooth and how quickly it is treated. If left untreated, the toothache may persist or even worsen.
What are the home remedies for this toothache?
Over-the-counter pain medication may help to alleviate the pain of a root canal-related toothache. However, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible to receive appropriate treatment.
When should you go see a dentist for this toothache?
If you are experiencing a toothache and suspect you may need a root canal, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible. A root canal-related toothache can be a sign of a more serious problem that requires immediate attention.
How is this toothache diagnosed?
A dentist can diagnose a root canal-related toothache by performing a physical examination and taking X-rays to assess the condition of the tooth and surrounding tissue.
What are the possible dental treatments for this toothache?
The treatment for a root canal-related toothache will depend on the severity of the infection or damage to the tooth. Options may include a root canal procedure, extraction of the tooth, or a filling or crown to repair the tooth.
What are some complications that result from a lack of treatment for this toothache?
If a root canal-related toothache is not treated, it can lead to further complications, such as the spread of infection or the loss of the tooth.
How do you prevent this toothache?
To prevent root canal-related toothaches, it is important to practice good oral hygiene, such as brushing your teeth twice a day and flossing daily. You should also visit your dentist regularly for cleanings and checkups. If you have a toothache that does not go away, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Infection

Infections in the mouth can be serious and can lead to a variety of toothaches. In this section of our encyclopedia, we will explore the different types of infections that can affect the teeth and gums, including abscessed teeth, gum infections, and tooth infections. We will also discuss the symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies for each type of infection. It is important to be aware of the signs of an infection in the mouth and to seek treatment as soon as possible to prevent the infection from spreading and causing more serious problems.
Abscess

What are the causes of this toothache?
An abscess is a pocket of pus that has formed around the tooth or in the gum tissue. It is typically caused by a bacterial infection that has spread from the tooth or gums to the surrounding tissue.
What are the symptoms of this toothache?
The main symptom of an abscess-related toothache is severe pain. You may also experience fever, swelling, and redness in the affected area.
What will irritate this toothache?
Anything that irritates the infected area, such as eating or drinking hot or cold foods or beverages, may exacerbate the pain of an abscess-related toothache.
How long will this toothache last?
The length of an abscess-related toothache will depend on the severity of the infection and how quickly it is treated. If left untreated, the toothache may persist or even worsen.
What are the home remedies for this toothache?
There are no effective home remedies for abscess-related toothaches. It is important to see a dentist as soon as possible to receive appropriate treatment.
When should you go see a dentist for this toothache?
If you are experiencing a toothache and suspect you may have an abscess, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible. Abscesses can be very serious and can spread quickly, so prompt treatment is essential.
How is this toothache diagnosed?
A dentist can diagnose an abscess by examining your teeth and gums, taking X-rays, and performing a physical examination.
What are the possible dental treatments for this toothache?
The treatment for an abscess will depend on the severity of the infection. Options may include draining the abscess, prescribing antibiotics, and performing root canal treatment or tooth extraction.
What are some complications that result from a lack of treatment for this toothache?
If an abscess is not treated, it can lead to more serious complications, such as the spread of the infection to other parts of the body or the development of sepsis, a potentially life-threatening condition.
How do you prevent this toothache?
To prevent abscesses and the resulting toothaches, it is important to practice good oral hygiene, such as brushing your teeth twice a day and flossing daily. You should also visit your dentist regularly for cleanings and checkups. If you have a toothache or other dental issue, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible to receive appropriate treatment.
Cavity
What are the causes of this toothache?
Tooth decay, or the breakdown of the enamel and dentin layers of the tooth, is the main cause of cavities and the resulting toothaches. Tooth decay is typically caused by bacteria in the mouth that produce acid, which erodes the tooth enamel.
What are the symptoms of this toothache?
The main symptom of a cavity-related toothache is a pain when biting or chewing. You may also experience sensitivity to hot or cold food or drinks.
What will irritate this toothache?
Eating or drinking anything sweet or cold may exacerbate the pain of a cavity-related toothache.
How long will this toothache last?
The length of a cavity-related toothache will depend on the severity of the decay and how quickly it is treated. If left untreated, the toothache may persist or even worsen.
What are the home remedies for this toothache?
Some home remedies for a cavity-related toothache include using over-the-counter pain medication, rinsing your mouth with warm salt water, or applying a cold compress to the affected area. However, these remedies are only temporary and will not address the underlying cause of the toothache.
When should you go see a dentist for this toothache?
If you are experiencing a toothache, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment. The sooner you see a dentist, the more likely it is that the tooth can be saved.
How is this toothache diagnosed?
A dentist can diagnose a cavity by examining your teeth and performing X-rays.
What are the possible dental treatments for this toothache?
The treatment for a cavity will depend on the severity of the decay. If the decay is caught in the early stages, your dentist may be able to repair the tooth with a filling. If the decay is more advanced, you may need a root canal or tooth extraction.
What are some complications that result from a lack of treatment for this toothache?
If a cavity is not treated, it can lead to more serious complications, such as an abscess (a pocket of pus) or the loss of the affected tooth.
How do you prevent this toothache?
To prevent cavities and the resulting toothaches, it is important to practice good oral hygiene, such as brushing your teeth twice a day and flossing daily. You should also visit your dentist regularly for cleanings and checkups. Limiting your intake of sugary foods and drinks can also help prevent cavities.
Gum Disease

What are the causes of this toothache?
Gum disease, also known as periodontitis, is an infection of the tissues that support the teeth. It is typically caused by bacteria in the mouth that produce plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that builds up on the teeth. If plaque is not removed through proper oral hygiene, it can harden into tartar, which can cause gum inflammation and infection.
What are the symptoms of this toothache?
Gum disease, also known as periodontitis, is an infection of the tissues that support the teeth. It is typically caused by bacteria in the mouth that produce plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that builds up on the teeth. If plaque is not removed through proper oral hygiene, it can harden into tartar, which can cause gum inflammation and infection.
What will irritate this toothache?
Anything that irritates the infected gums, such as eating or drinking hot or cold foods or beverages, may exacerbate the pain of a gum disease-related toothache.
How long will this toothache last?
The length of a gum disease-related toothache will depend on the severity of the infection and how quickly it is treated. If left untreated, the toothache may persist or even worsen.
What are the home remedies for this toothache?
Some home remedies for a gum disease-related toothache include using over-the-counter pain medication, rinsing your mouth with warm salt water, or applying a cold compress to the affected area. However, these remedies are only temporary and will not address the underlying cause of the toothache.
When should you go see a dentist for this toothache?
If you are experiencing a toothache, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment. The sooner you see a dentist, the more likely it is that the toothache can be effectively treated.
How is this toothache diagnosed?
A dentist can diagnose gum disease by examining your teeth and gums, taking X-rays, and performing a gum pocket measurement.
What are the possible dental treatments for this toothache?
The treatment for gum disease will depend on the severity of the infection. Options may include deep cleaning, medication, or surgery.
What are some complications that result from a lack of treatment for this toothache?
If gum disease is not treated, it can lead to more serious complications, such as tooth loss and bone loss.
How do you prevent this toothache?
To prevent gum disease and the resulting toothaches, it is important to practice good oral hygiene, such as brushing your teeth twice a day and flossing daily. You should also visit your dentist regularly for cleanings and checkups. Avoiding tobacco products and controlling conditions such as diabetes can also help prevent gum disease.
Sinus

What are the causes of this toothache?
A sinus toothache is typically caused by inflammation or infection in the sinuses, which are air-filled cavities in the bones of the face. Sinusitis, or inflammation of the sinuses, can be caused by a viral or bacterial infection, allergies, or structural abnormalities in the sinuses.
What are the symptoms of this toothache?
The main symptom of a sinus toothache is a constant or intermittent throbbing pain in the teeth and jaws. You may also experience nasal congestion and pressure in the face.
What will irritate this toothache?
Anything that irritates the inflamed sinuses, such as changes in altitude, cold or dry air, or exposure to irritants such as smoke or pollution, may exacerbate the pain of a sinus toothache.
How long will this toothache last?
The length of a sinus toothache will depend on the underlying cause and how quickly it is treated. If left untreated, the toothache may persist or even worsen.
What are the home remedies for this toothache?
Some home remedies for a sinus toothache include using over-the-counter pain medication, using a saline nasal spray or humidifier to help alleviate congestion, and applying a warm or cold compress to the affected area. However, these remedies are only temporary and will not address the underlying cause of the toothache.
When should you go see a dentist for this toothache?
If you are experiencing a toothache and have other symptoms of sinusitis, such as congestion and pressure in the face, you should see a healthcare provider. If your toothache is caused by a dental issue, such as a cavity or gum disease, you should see a dentist.
How is this toothache diagnosed?
A healthcare provider or dentist can diagnose a sinus toothache by examining your teeth and gums, performing a physical examination, and taking X-rays. They may also order a CT scan or other imaging tests to assess the sinuses.
What are the possible dental treatments for this toothache?
If your sinus toothache is caused by a dental issue, such as a cavity or gum disease, your dentist will recommend the appropriate treatment.
What are some complications that result from a lack of treatment for this toothache?
If a sinus infection is not treated, it can lead to more serious complications, such as meningitis or an abscess in the sinuses.
How do you prevent this toothache?
To prevent sinus infections and the resulting toothaches, it is important to practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently and avoiding close contact with people who are sick. Avoiding tobacco products and controlling conditions such as allergies and asthma can also help prevent sinusitis. If you have structural abnormalities in your sinuses, such as a deviated septum, your healthcare provider may recommend surgery to correct them.
Tonsilitis

What are the causes of this toothache?
Tonsilitis is an infection of the tonsils, which are small glands located in the back of the throat. It is typically caused by a viral or bacterial infection.
What are the symptoms of this toothache?
The main symptom of tonsilitis-related toothaches is a pain when swallowing. You may also experience fever, a sore throat, and swollen tonsils.
What will irritate this toothache?
Anything that irritates the infected tonsils, such as eating or drinking hot or cold foods or beverages, may exacerbate the pain of a tonsilitis-related toothache.
How long will this toothache last?
The length of a tonsilitis-related toothache will depend on the underlying cause and how quickly it is treated. If left untreated, the toothache may persist or even worsen.
What are the home remedies for this toothache?
Some home remedies for tonsilitis-related toothaches include using over-the-counter pain medication, drinking warm liquids to help alleviate soreness, and using a humidifier to help moisten the air. However, these remedies are only temporary and will not address the underlying cause of the toothache.
When should you go see a dentist for this toothache?
If you are experiencing a toothache and suspect you may have tonsilitis, it is important to see a healthcare provider. A dentist is not typically involved in the treatment of tonsilitis.
How is this toothache diagnosed?
A healthcare provider can diagnose tonsilitis by examining your throat and performing a physical examination. They may also order a throat culture or other tests to confirm the diagnosis.
What are the possible dental treatments for this toothache?
There are no specific dental treatments for tonsilitis. The treatment will depend on the underlying cause and may include antibiotics or other medications.
What are some complications that result from a lack of treatment for this toothache?
If tonsilitis is not treated, it can lead to more serious complications, such as an abscess in the tonsils or the spread of the infection to other parts of the body.
How do you prevent this toothache?
To prevent tonsilitis and the resulting toothaches, it is important to practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently and avoiding close contact with people who are sick. Avoiding tobacco products and controlling conditions such as allergies and asthma can also help prevent tonsilitis. If you have a weakened immune system, you may be more susceptible to tonsilitis and other infections. In this case, your healthcare provider may recommend vaccines or other measures to help boost your immune system.
Physical Stress

Physical stress can have a significant impact on our oral health and can lead to a variety of toothaches. In this section of our encyclopedia, we will explore the various types of toothaches that can be caused by physical stress, including grinding or clenching the teeth, jaw joint problems, and trauma to the teeth. We will also discuss the symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies for each type of toothache. It is important to understand the role of physical stress in dental problems and to seek treatment if you are experiencing toothaches related to this type of stress.
Cracked Tooth
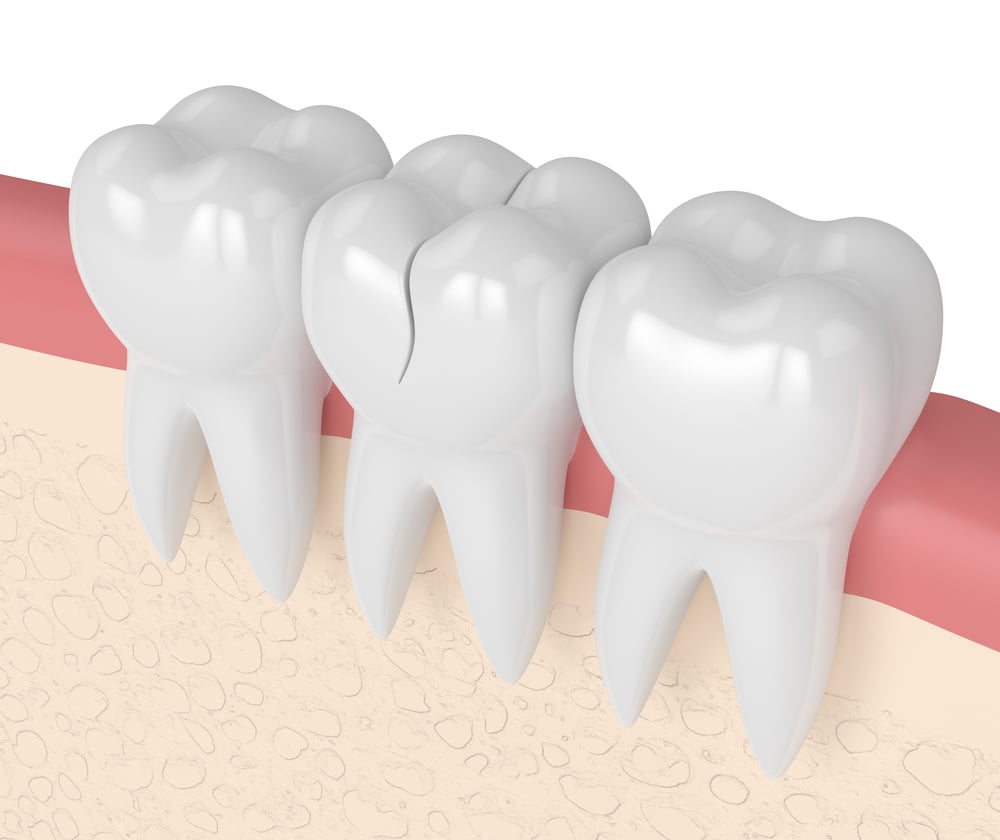
What are the causes of this toothache?
A cracked tooth can be caused by a variety of factors, including biting down on hard objects, grinding the teeth, and experiencing trauma to the mouth.
What are the symptoms of this toothache?
Symptoms of a cracked tooth may include pain when biting or chewing, sensitivity to hot or cold food or drinks, and a sensation of something stuck between the teeth.
What will irritate this toothache?
Biting or chewing may irritate a cracked tooth, as well as consuming hot or cold foods or drinks.
How long will this toothache last?
A cracked tooth may cause ongoing pain until it is treated.
What are the home remedies for this toothache?
Home remedies for a cracked tooth may include taking over-the-counter pain medication and avoiding biting or chewing on the affected tooth. However, these remedies are only temporary and should not be used as a substitute for professional dental treatment.
When should you go see a dentist for this toothache?
If you are experiencing a cracked tooth, you should see a dentist as soon as possible. Prompt treatment can help prevent the toothache from worsening and can help prevent further damage to the tooth.
How is this toothache diagnosed?
A dentist will diagnose a cracked tooth by examining the tooth and performing diagnostic tests, such as X-rays, to assess the extent of the crack.
What are the possible dental treatments for this toothache?
Possible dental treatments for a cracked tooth may include filling the crack, placing a crown or cap on the tooth to protect it, or extracting the tooth if it is severely damaged and cannot be repaired.
What are some complications that result from a lack of treatment for this toothache?
If a cracked tooth is not treated, it can lead to further damage to the tooth and the surrounding tissue, as well as the development of an infection.
How do you prevent this toothache?
To prevent a cracked tooth, it is important to practice good oral hygiene, including brushing and flossing regularly, avoid biting down on hard objects, and wear a mouthguard when playing contact sports. It is also important to seek prompt dental treatment if you experience any trauma to the teeth.
Impacted Tooth

What are the causes of this toothache?
An impacted tooth is a tooth that is unable to fully emerge from the gums due to blockages such as other teeth, gum tissue, or jawbone. This can occur with any type of tooth, but it is most common with wisdom teeth.
What are the symptoms of this toothache?
The main symptom of an impacted tooth is a pain when biting or chewing. Other symptoms may include swelling and redness around the gums, difficulty opening the mouth, and bad breath.
What will irritate this toothache?
Eating or drinking hard or crunchy foods may irritate an impacted tooth and cause pain.
How long will this toothache last?
The length of time that the toothache lasts will depend on the severity of the impact and the effectiveness of treatment. In some cases, the toothache may resolve on its own if the tooth is able to emerge from the gums. However, if the tooth is fully impacted and treatment is not received, the toothache may continue indefinitely.
What are the home remedies for this toothache?
Over-the-counter pain medication may help to alleviate the discomfort of an impacted tooth. Applying a cold compress to the area may also help to reduce swelling. However, these remedies will not resolve the underlying issue, and it is important to see a dentist for proper treatment.
When should you go see a dentist for this toothache?
If you are experiencing pain or discomfort in your mouth that you suspect may be caused by an impacted tooth, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible.
How is this toothache diagnosed?
A dentist will examine your mouth and may take X-rays to determine the cause of the toothache.
What are the possible dental treatments for this toothache?
Treatment for an impacted tooth may include removing any blockages to allow the tooth to emerge or extracting the tooth if it is unable to emerge.
What are some complications that result from a lack of treatment for this toothache?
If an impacted tooth is not treated, it can lead to infection, damage to surrounding teeth, and the formation of cysts or tumors.
How do you prevent this toothache?
To prevent an impacted tooth, it is important to practice good oral hygiene, including brushing and flossing regularly and to see a dentist regularly for cleanings and check-ups. In some cases, your dentist may recommend the removal of wisdom teeth to prevent future impactions.
Myalgia

What are the causes of this toothache?
Myalgia is a general term for muscle pain and can occur in any muscle in the body, including the muscles of the jaw and face. Myalgia can be caused by a variety of factors, including overuse or strain, poor posture, stress, and certain medical conditions. In the case of the jaw and facial muscle pain, myalgia may be caused by grinding or clenching the teeth or by tension in the jaw muscles due to stress or other factors.
What are the symptoms of this toothache?
The main symptom of myalgia is a pain when biting or chewing, as well as muscle stiffness or tenderness in the jaw and face.
What will irritate this toothache?
Eating or drinking hard or crunchy foods, or biting down with excessive force, may irritate muscles with myalgia and cause pain.
How long will this toothache last?
The length of time that the toothache lasts will depend on the severity of the muscle pain and the effectiveness of treatment. In some cases, myalgia may resolve on its own with rest and self-care. However, if the underlying cause is not addressed, the muscle pain may recur.
What are the home remedies for this toothache?
Resting the muscles and applying heat or cold to the affected area may help to alleviate the discomfort of myalgia. Over-the-counter pain medication may also provide relief.
When should you go see a dentist for this toothache?
If you are experiencing muscle pain in your jaw and face that persists despite self-care measures, it is important to see a dentist or healthcare provider to determine the cause and receive proper treatment.
How is this toothache diagnosed?
A dentist or healthcare provider will examine your mouth and may take X-rays or other tests to determine the cause of the pain.
What are the possible dental treatments for this toothache?
Treatment for myalgia may include medications to control the pain, physical therapy to stretch and strengthen the muscles, and treatment for any underlying causes, such as grinding or clenching the teeth.
What are some complications that result from a lack of treatment for this toothache?
If myalgia is not treated, the muscle pain may persist and may lead to other problems such as difficulty eating and speaking and tension headaches.
How do you prevent this toothache?
To prevent myalgia, it is important to practice good posture, manage stress, and avoid overusing or straining the muscles of the jaw and face. In addition, practicing good oral hygiene and seeing a dentist regularly for check-ups may help to prevent or detect any underlying conditions that may contribute to the development of myalgia.
Pulpits
What are the causes of this toothache?
Pulpitis is an inflammation of the pulp, the innermost layer of the tooth that contains the nerves and blood vessels. Pulpitis can be caused by a variety of factors, including tooth decay, injury to the tooth, and gum disease.
What are the symptoms of this toothache?
The main symptom of pulpitis is severe pain, which may be constant or intermittent. Pulpitis may also cause sensitivity to hot or cold food or drinks.
What will irritate this toothache?
Eating or drinking hot or cold foods and drinks, or biting down on hard or crunchy foods, may irritate a tooth with pulpitis and cause pain.
How long will this toothache last?
The length of time that the toothache lasts will depend on the severity of the inflammation and the effectiveness of treatment. If left untreated, pulpitis may progress to a more severe form of infection known as an abscessed tooth.
What are the home remedies for this toothache?
Over-the-counter pain medication may help to alleviate the discomfort of pulpitis. Applying a cold compress to the area may also help to reduce swelling. However, these remedies will not resolve the underlying issue, and it is important to see a dentist for proper treatment.
When should you go see a dentist for this toothache?
If you are experiencing severe pain in your mouth that you suspect may be caused by pulpitis, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible.
How is this toothache diagnosed?
A dentist will examine your mouth and may take X-rays to determine the cause of the toothache.
What are the possible dental treatments for this toothache?
Treatment for pulpitis may include a filling, root canal, or tooth extraction, depending on the severity of the inflammation.
What are some complications that result from a lack of treatment for this toothache?
If pulpitis is not treated, it can lead to an abscessed tooth, which is a severe infection that can spread to other areas of the body and cause serious health problems.
How do you prevent this toothache?
To prevent pulpitis, it is important to practice good oral hygiene, including brushing and flossing regularly, and to see a dentist regularly for cleanings and check-ups. Early detection and treatment of tooth decay and gum disease can help to prevent pulpitis.
Teeth Grinding (Bruxism)

What are the causes of this toothache?
Teeth grinding, or bruxism is caused by the constant grinding or clenching of the teeth, often during sleep. It can also be caused by stress, anxiety, or certain medications.
What are the symptoms of this toothache?
Symptoms of a teeth-grinding-related toothache may include constant or intermittent throbbing pain, sensitivity to hot or cold food or drinks, and a clicking or popping sound when you move your jaw.
What will irritate this toothache?
Grinding or clenching the teeth can irritate a teeth-grinding-related toothache.
How long will this toothache last?
A teeth-grinding-related toothache may last as long as the grinding or clenching continues.
What are the home remedies for this toothache?
Home remedies for a teeth-grinding-related toothache may include taking over-the-counter pain medication, avoiding hard or chewy foods, and practicing stress-reducing techniques such as relaxation or deep breathing. However, these remedies are only temporary and should not be used as a substitute for professional dental treatment.
When should you go see a dentist for this toothache?
If you are experiencing a teeth grinding-related toothache, you should see a dentist as soon as possible. A dentist can help diagnose the cause of the toothache and recommend the appropriate treatment.
How is this toothache diagnosed?
A dentist will diagnose a teeth grinding-related toothache by examining the teeth and performing diagnostic tests, such as X-rays, to assess the extent of the damage.
What are the possible dental treatments for this toothache?
Possible dental treatments for a teeth grinding-related toothache may include the use of a mouthguard to protect the teeth from grinding, dental restorations to repair damaged teeth, and stress-management techniques to help reduce grinding.
What are some complications that result from a lack of treatment for this toothache?
If a teeth grinding-related toothache is not treated, it can lead to further damage to the teeth, such as cracks, chips, and wear, as well as to the surrounding tissue.
How do you prevent this toothache?
To prevent a teeth-grinding-related toothache, it is important to address the underlying cause of the grinding, such as stress or anxiety. A dentist may recommend the use of a mouthguard to protect the teeth while you sleep and may also recommend stress-management techniques to help reduce grinding.
Teething
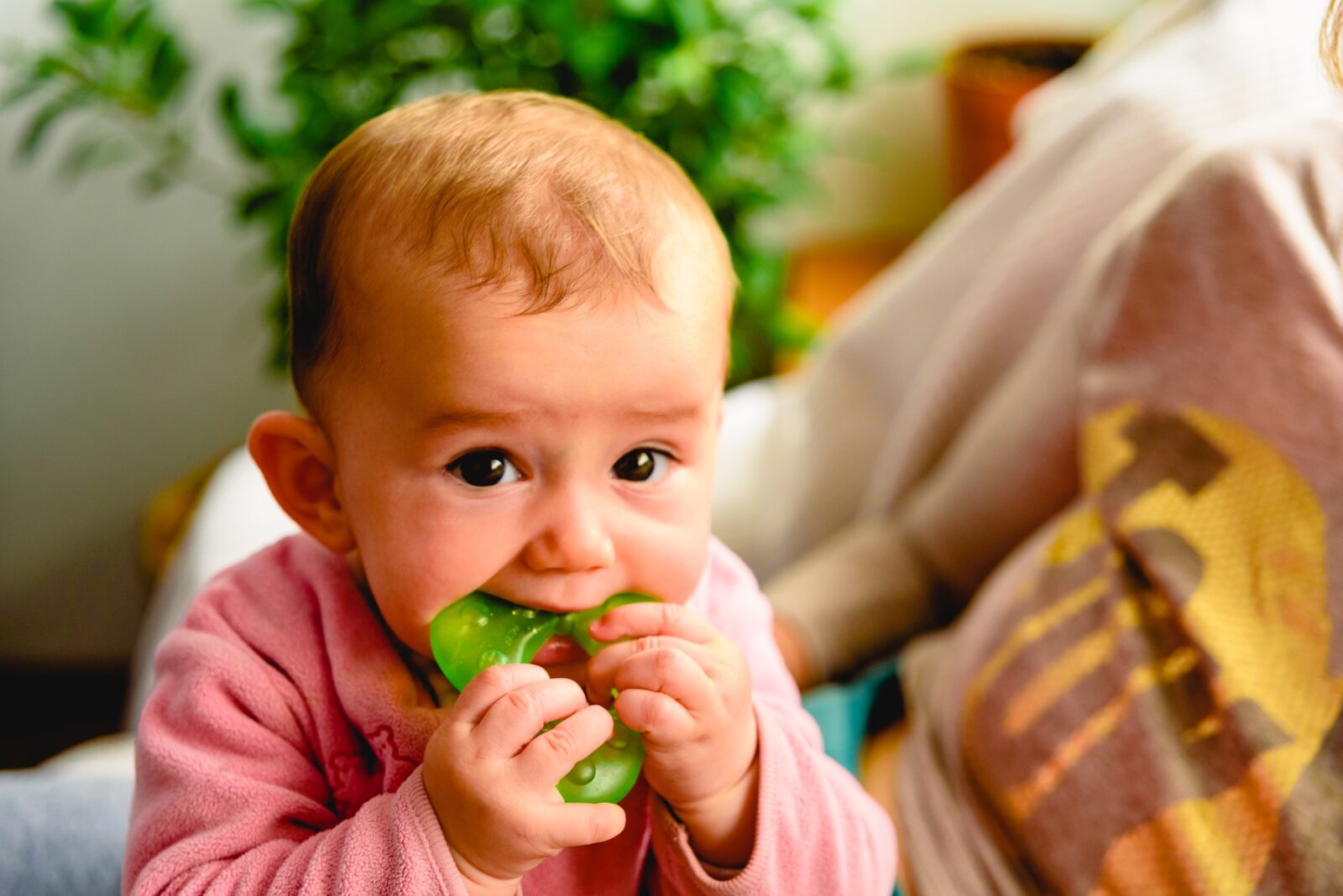

What are the causes of this toothache?
Teething is the process of introducing primary teeth, or baby teeth, into the mouth, and it is a common occurrence in infants and young children. The process of teething can cause discomfort and pain in the gums.
What are the symptoms of this toothache?
Symptoms of teething may include pain, irritability, difficulty sleeping, and drooling.
What will irritate this toothache?
Teething is an ongoing process, and the discomfort associated with it may be constant or intermittent.
How long will this toothache last?
Teething typically begins around 6 months of age and can continue until the child is 3 years old. The duration of teething will depend on the child’s individual development.
What are the home remedies for this toothache?
Home remedies for teething-related discomfort may include giving the child a clean, cool teething ring or a wet washcloth to chew on or applying a small amount of teething gel to the gums. Over-the-counter pain medication may also be recommended by a healthcare provider.
When should you go see a dentist for this toothache?
If you are concerned about your child’s teething-related discomfort, you should speak with a healthcare provider or a dentist.
How is this toothache diagnosed?
Teething does not typically require a diagnosis, as it is a normal part of childhood development.
What are the possible dental treatments for this toothache?
There are no specific dental treatments for teething, as it is a normal part of childhood development. However, a healthcare provider or a dentist may recommend remedies to help manage the discomfort associated with teething.
What are some complications that result from a lack of treatment for this toothache?
There are no known complications that result from a lack of treatment for teething.
How do you prevent this toothache?
Teething is a natural part of childhood development and cannot be prevented. However, you can help manage the discomfort associated with teething by providing your child with clean, cool objects to chew on, such as a teething
TMJ (Temporomandibular Joint) Disorder

What are the causes of this toothache?
TMJ disorder is caused by a problem with the joint that connects the jaw to the skull, which can result from a variety of factors, including the misalignment of the jaw, injury, or arthritis.
What are the symptoms of this toothache?
Symptoms of TMJ disorder may include pain when biting or chewing, clicking or popping in the jaw, difficulty opening the mouth, and a sensation of something stuck between the teeth.
What will irritate this toothache?
Biting or chewing may irritate a toothache caused by TMJ disorder.
How long will this toothache last?
The duration of a toothache caused by TMJ disorder will depend on the severity of the disorder and the treatment received.
What are the home remedies for this toothache?
Home remedies for a toothache caused by TMJ disorder may include taking over-the-counter pain medication, avoiding hard or chewy foods, and applying a warm compress to the outside of the jaw to help relax the muscles. However, these remedies are only temporary and should not be used as a substitute for professional dental treatment.
When should you go see a dentist for this toothache?
If you are experiencing a toothache caused by TMJ disorder, you should see a dentist as soon as possible. A dentist can help diagnose the cause of the toothache and recommend the appropriate treatment.
How is this toothache diagnosed?
A dentist will diagnose TMJ disorder by examining the jaw and performing diagnostic tests, such as X-rays, to assess the condition of the joint.
What are the possible dental treatments for this toothache?
Possible dental treatments for a toothache caused by TMJ disorder may include the use of a mouthguard to protect the teeth from grinding, dental restorations to repair damaged teeth, and physical therapy or other exercises to help improve the function of the jaw.
What are some complications that result from a lack of treatment for this toothache?
If a toothache caused by TMJ disorder is not treated, it can lead to further damage to the teeth and the surrounding tissue, as well as to the joint itself.
How do you prevent this toothache?
To prevent a toothache caused by TMJ disorder, it is important to practice good oral hygiene, including brushing and flossing regularly, and seek treatment for any underlying issues, such as misalignment of the jaw or arthritis. It is also important to avoid biting down on hard objects and to practice stress-reducing techniques to help prevent grinding or clenching of the teeth.
TN (Trigeminal Neuralgia)

What are the causes of this toothache?
Trigeminal neuralgia, also known as TN or tic douloureux, is a type of chronic pain that affects the trigeminal nerve, which is the nerve that provides sensation to the face, mouth, and jaw. The exact cause of TN is often unknown, but it may be caused by irritation or damage to the trigeminal nerve, compression of the nerve by a blood vessel, or a brain lesion.
What are the symptoms of this toothache?
The main symptom of TN is severe, intermittent facial pain that may be triggered by activities such as eating, speaking, or touching the face. Other symptoms may include numbness or tingling in the jaw and a sensation of shock-like pain.
What will irritate this toothache?
TN is often triggered by activities that stimulate the trigeminal nerve, such as eating, speaking, or touching the face.
How long will this toothache last?
TN is a chronic condition, which means that the pain may come and go over a long period of time. The frequency and severity of the pain may vary from person to person.
What are the home remedies for this toothache?
Over-the-counter pain medication may help to alleviate the discomfort of TN. Applying a cold compress to the area may also help to reduce swelling. However, these remedies will not resolve the underlying issue, and it is important to see a dentist or a healthcare provider for proper treatment.
When should you go see a dentist for this toothache?
If you are experiencing severe, intermittent pain in your face that you suspect may be caused by TN, it is important to see a dentist or a healthcare provider as soon as possible.
How is this toothache diagnosed?
A dentist or healthcare provider will examine your mouth and may take X-rays or other tests to determine the cause of the pain.
What are the possible dental treatments for this toothache?
Treatment for TN may include medications to control the pain, nerve blocks to numb the area, or surgery to remove the source of irritation or compression.
What are some complications that result from a lack of treatment for this toothache?
If TN is not treated, the pain may continue and may become more severe over time. In some cases, TN may cause difficulty eating and speaking and may lead to depression and anxiety.
How do you prevent this toothache?
It is not always possible to prevent TN, as the exact cause is often unknown. However, maintaining good oral hygiene and seeing a dentist regularly for check-ups may help to prevent or detect any underlying conditions that may contribute to the development of TN.
Conclusion
In conclusion, toothaches are a common problem that can be caused by a variety of factors, including tooth decay, gum disease, sinusitis, abscesses, tonsillitis, dental treatment-related issues, and more. Toothaches can be accompanied by a range of symptoms, including pain, sensitivity, swelling, and redness. While some toothaches can be treated with home remedies, it is important to see a dentist for proper diagnosis and treatment. Untreated toothaches can lead to further complications and damage to the tooth, so it is important to address the issue as soon as possible. Good oral hygiene and regular dental checkups can help to prevent toothaches and maintain the health of your teeth and gums.