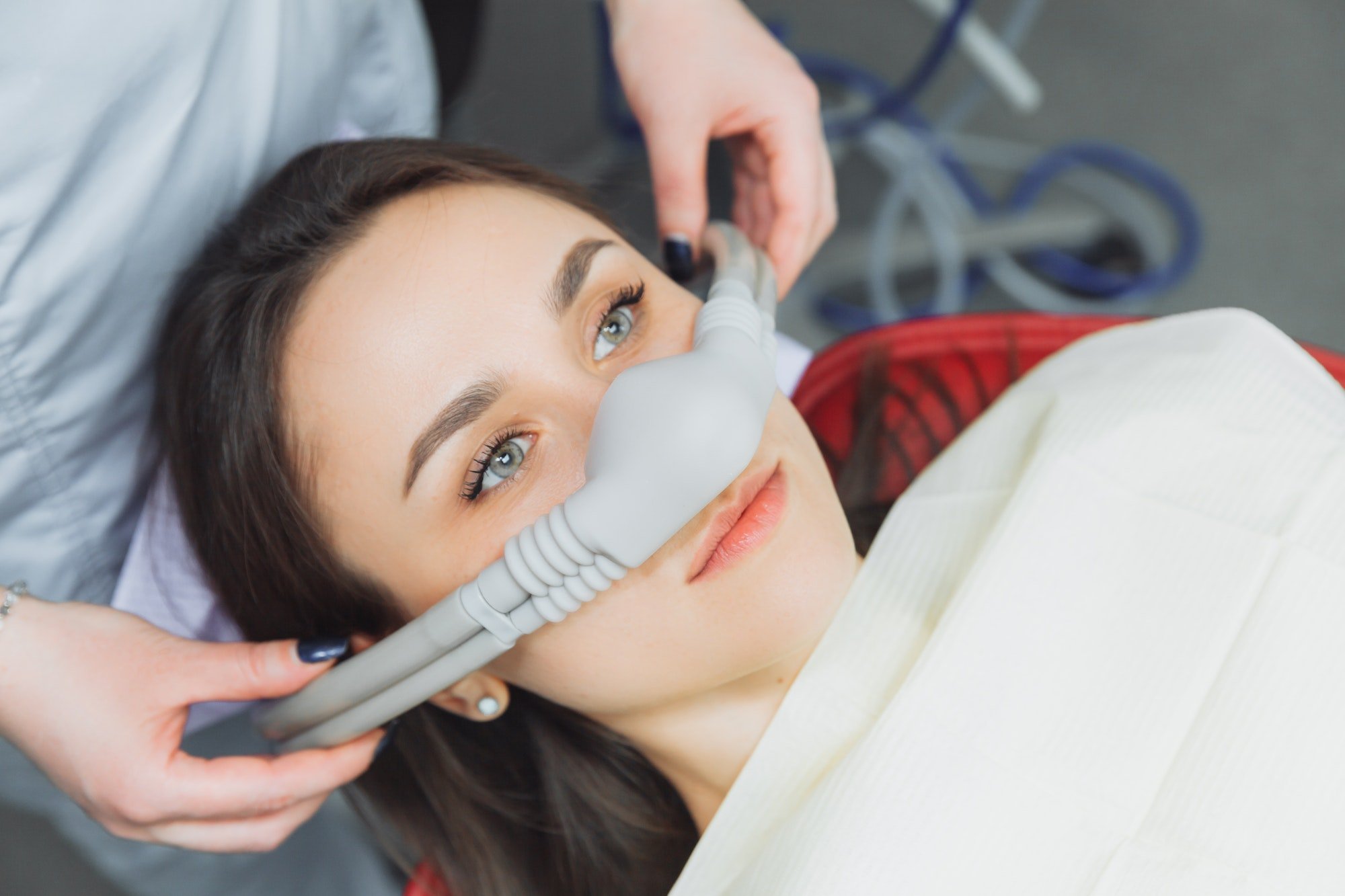
Overview of Dental Sedation
Dental sedation is a type of medication that is used to help patients relax during dental procedures. It is often used for patients who have dental anxiety or for complex dental procedures that may be more comfortable with the help of sedation. Dental sedation can be administered in several ways, including through inhalation, orally, or intravenously. The type of sedation used may depend on the patient’s medical history, the complexity of the procedure, and the patient’s preferences.
Dental sedation can help make the dental experience more comfortable and reduce anxiety or discomfort during the procedure. It can also help patients relax and make it easier for the dentist to complete the procedure. However, it is important to note that dental sedation does not eliminate pain completely. Some patients may still experience some discomfort or pressure during the procedure, and local anesthesia may still be used in addition to sedation.
Overall, dental sedation can be a helpful option for patients who are anxious or nervous about dental procedures or who need to undergo complex procedures. It is important to discuss the options for dental sedation with your dentist and to understand the risks and precautions associated with each type of sedation.
Table of Dental Sedation
| Type | Method of Administration | Indications | Benefits | Risks | Effects | Prohibited Patients |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrous oxide | Inhaled through a mask placed over the nose | Mild to moderate dental anxiety or shorter procedures | Quick to take effect and easy to adjust the level of sedation as needed | Nausea, dizziness | Mild sedative | Patients with certain medical conditions, such as asthma or COPD, patients who are pregnant or breastfeeding, or patients who have recently used alcohol or recreational drugs |
| Oral sedation | Taken orally before the procedure | Moderate to severe dental anxiety or longer procedures | Can help patients relax and reduce anxiety during the procedure | Drowsiness, dry mouth, constipation | Sedative or a combination of a sedative and an anti-anxiety medication | Patients with certain medical conditions, such as sleep apnea or liver disease, or patients who have recently used alcohol or recreational drugs |
| Intravenous (IV) sedation | Administered through a vein | Severe dental anxiety or complex procedures that require a longer appointment | Allows the dentist to adjust the level of sedation as needed during the procedure | Nausea, dizziness, drowsiness | Sedative | Patients with certain medical conditions, such as sleep apnea or liver disease, or patients who have recently used alcohol or recreational drugs |
| General anesthesia | Administered through an injection or inhaled through a mask | Complex or lengthy procedures or patients who cannot tolerate other forms of sedation | Causes a loss of consciousness and memory of the procedure | Nausea, vomiting, sore throat | General anesthesia | Patients with certain medical conditions, such as sleep apnea or liver disease, or patients who have recently used alcohol or recreational drugs |
Alternatives to Dental Sedation
For some patients, dental sedation may not be an option due to medical conditions, allergies, or other factors. In these cases, there are alternatives to dental sedation that can help patients relax and feel more comfortable during dental procedures. Some alternatives to dental sedation include:
- Distraction techniques: Distraction techniques, such as listening to music or watching a movie, can help distract patients from the sounds and sensations of the dental procedure.
- Relaxation techniques: Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation, can help patients calm their minds and bodies during the procedure.
- Communication with the dental team: Open communication with the dental team can help patients feel more at ease and in control of the procedure. Patients should feel free to ask questions, express their concerns, and communicate their needs to the dental team.
- Sedative-free dentistry: Some dentists offer sedative-free dentistry, which aims to provide dental care without the use of sedative medications. This approach may involve the use of alternative techniques, such as acupuncture or hypnotherapy, to help patients relax during the procedure.
By understanding the alternatives to dental sedation, patients can explore options that may be more suitable for their needs and preferences. It is important to discuss the options for dental sedation with your dentist and to understand the risks and benefits of each approach.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dental sedation can be a helpful option for patients who are anxious or nervous about dental procedures or who need to undergo complex procedures. By understanding the different types of dental sedation and their indications, benefits, risks, and other considerations, patients can make informed decisions about the best approach for their dental care. It is important to discuss the options for dental sedation with your dentist and to understand the risks and precautions associated with each type of sedation. Whether you choose nitrous oxide, oral sedation, IV sedation, or general anesthesia, it is important to follow your dentist’s instructions and to disclose any medical conditions or medications that may affect your ability to undergo dental sedation. For some patients, dental sedation may not be an option due to medical conditions, allergies, or other factors. In these cases, there are alternatives to dental sedation, such as distraction techniques, relaxation techniques, open communication with the dental team, and sedative-free dentistry, that can help patients relax and feel more comfortable during dental procedures. Proper dental care, including regular visits to the dentist and good oral hygiene practices, can help prevent the need for dental sedation and maintain the health of your teeth and gums.